 Genital Tuberculosis
Genital Tuberculosis
Genital TB is a bacterial infection. It affects the female genital organs – ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina – or the surrounding lymph nodes in the pelvis. It is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A tuberculin skin test is performed to detect the presence of TB anywhere in the body. Its diagnosis method depends upon the site of infection. Chest X-ray, pelvic ultrasound scan, endometrial curettage, cervical smear examination, menstrual blood analysis and laparoscopic or endoscopic examination of the genital organs may also have to be done to know the condition.
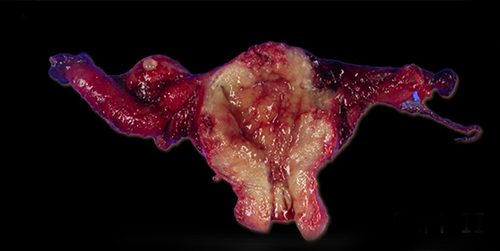
Genital TB can only be treated by making sure that no other part of the body is affected by TB. This means that females should take precautions against lung TB even at a young age. Surgical treatment of the genital parts may be required in the advanced stages of the condition.
